Disaccharide
A disaccharide (also called a double sugar ) is the sugar formed when two monosaccharides (simple sugars) are joined by glycosidic linkage. Like monosaccharides, disaccharides are soluble in water. Three common examples are sucrose, lactose, and maltose.
| CAS Number |
Product Name |
Structure |
Purity |
Pricing |
| N.A |
(3S,4R,5R,6S)-2-(((3R,4R,5S,6R)-3-acetamido-5-hydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-2-((6-methoxy-6-oxohexyl)oxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-yl)oxy)-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triyl triacetate |
 |
95-98% |
Pricing
|
| N.A |
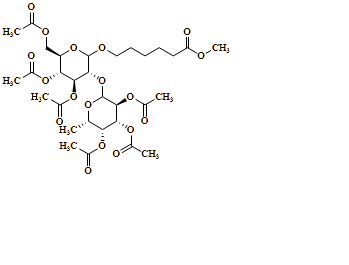
(3S,4R,5R,6S)-2-(((3R,4S,5R,6R)-4,5-diacetoxy-6-(acetoxymethyl)-2-((6-methoxy-6-oxohexyl)oxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3-yl)oxy)-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triyl triacetate |
 |
95-98% |
Pricing
|
| N.A |
(3S,4R,5R,6S)-2-(((3R,4S,5R,6R)-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-2-((6-methoxy-6-oxohexyl)oxy)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3-yl)oxy)-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triyl triacetate |
 |
95-98% |
Pricing
|